datngbn1226
Jun 1, 2023
Writing Feedback / The diagram belows show the water cycle, which is the continuous movement of water on [2]
Test:The diagram belows show the water cycle, which is the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the earth.
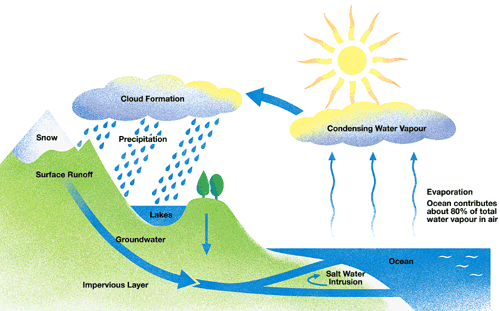
The picture illustrates the natural cycle of water passing from ocean to air to land during the natural environment.
Overall, the water experience three main stages which are shown on the diagram. Ocean water evaporates, falls as rain, and then runs back into the ocean again.
Beginning at the first stage, about 80% of water vapor in the air derives from the oceans. Heat from the sun transfers water from liquid to steam and then condenses to clouds. At the second stage, white clouds become heavier to turn into the dark clouds, then water falls as rain or snow.
At the third stage in the cycle, rainwater can move in various ways. Some of it may pour into lakes or return to the seas via the path called ' surface runoff'. Otherwise, rainwater may seep into the ground, reaching the impervious layer of the earth. Salt water intrusion is shown to take place before groundwater passes into the seas to complete the cycle.
the water cycle diagram
Test:The diagram belows show the water cycle, which is the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the earth.
The picture illustrates the natural cycle of water passing from ocean to air to land during the natural environment.
Overall, the water experience three main stages which are shown on the diagram. Ocean water evaporates, falls as rain, and then runs back into the ocean again.
Beginning at the first stage, about 80% of water vapor in the air derives from the oceans. Heat from the sun transfers water from liquid to steam and then condenses to clouds. At the second stage, white clouds become heavier to turn into the dark clouds, then water falls as rain or snow.
At the third stage in the cycle, rainwater can move in various ways. Some of it may pour into lakes or return to the seas via the path called ' surface runoff'. Otherwise, rainwater may seep into the ground, reaching the impervious layer of the earth. Salt water intrusion is shown to take place before groundwater passes into the seas to complete the cycle.
6a0120a5bb05d8970c01.gif
