Dear Isai,
The English language's tenses are 17. Down below I'll be showing you the tenses and their usage.
Simple Present / Present Progressive (or Continuous) / Simple Past / Past Progressive / Present Perfect / Present Perfect Progressive / Past Perfect / Past Perfect Progressive / Simple Future I (Will) / Simple Future I (Going to) / Future I Progressive / Simple Future II / Future II Progressive / Conditional I Simple / Conditional I Progressive / Conditional II Simple / Conditional II Progressive.
Basically, to figure out in what tense you should conjugate the verb, you need to look for any time indications (e.g. today, tomorrow)
1/
Simple present (a.k.a. present tense):
*
Action occurring at an exact and immediate time once (Affirmative form), never (Negative form), several times (Question).*
General truth: an information that is widely known and take part in the common knowledge (e.g. The earth is round / Drugs are prejudicial ...)
*
Sayings and cliches: (Go hit the books, they don't hit back [Cliché] / A bird in hand is worth two in the bush [Saying])
*
Medical prescriptions and day-to-day advices.--> Conjugation: (Affirmative)
* All verbs (except "to be", "to have"):- I, he, she, it --> -s (verb + s) / e.g. to eat: He eats, she eats, it eats.
- I, you, we, they --> verb [without changes] (-to) / e.g. to talk: I talk, you talk, they talk, we talk.
* Verb "to be": I am ('m), you are ('re), they are ('re), we are ('re), he is ('s), she is ('s), it is ('s) { Avoid using contractions in academic writing.
* Verb "to have": I have ('ve), you have ('ve), we have ('ve), they have ('ve), he has ('s), she has ('s), it has ('s) { Avoid using contractions in academic writing.
P.S: Verbs, that ends up with an "h", takes an "e" before the "s" with: he, she, it.2/
Present progressive:*
Action occurring at the present time and taking a limited period of time [the action is not immediate] (e.g. Isai is jogging all along the forest).
*
Action taking place at the moment of speaking (e.g. The press are exclusively covering Orlando's gay club attacks).
*
Action arranged for the future (e.g. The senate elections results are announced soon).
--> Conjugation: (Affirmative)
All verbs (No exceptions):
* Verb "to be" conjugated with the given pronoun + the initial verb (-to) (e.g. He is struggling / They are performing a theater play / I am feeling better)
3/ Simple past (a.k.a. Past tense):*
Action taking place in the past, at a precise moment, once (Affirmative form),
never (Affirmative form) or
several times (Question) (e.g. I had a nightmare, last night / I didn't visit my uncle, during summer vacations / Did they win their game?)
*
Action taking place in the middle of another (e.g. If I
talked , they would have asphyxiate me to death)
--> Conjugation:
* Affirmative form : (Regular verbs): [All pronouns] verb+ed (e.g. I talked / they watched / We managed / you eliminated)
(Irregular verbs): [Here is the list of all irregular verbs I could help you with]: "Check out the attached PDF file herewith".
* Negative form : (All verbs without exceptions): Verb "to do" in the past tense (did) + not + the initial verb (-to) (e.g. Ecologic meeting didn't give much of solution to fix the seriously dangerous environmental crisis / The majority in the Congress didn't decide to disable the discussed law ...)
* Interrogative form (Question): Verb "to do" in the past tense (did) + subject + the initial verb (-to) (Did you finish your homework? / Did my mother arrived home?).
4/ *
Past Perfect Simple:* Action taking place before a certain time in the past (e.g. He had visited her before she told the police to intervene)
*
It can be interchangeable with the past perfect progressive.*
Putting emphasis on the fact (the past perfect progressive focuses on the duration of the event).
5/ *
Future Tense (going to): (a.k.a. Future Simple):
*
Decision made for the future / Planning (e.g. I am going to visit the gymnasium later)
*
Conclusion with regard to the future (e.g. He got low GPA and SAT scores, he is, definitely, not going to apply for top-class colleges)
--> Conjugation:
* Affirmative: verb "to be" + going to (e.g. The president is going to leave the white house as soon as the new elected president do the sworn statement).
* Interrogative: verb "to be" + subject + going to (e.g. Is he going to have his stomach fed in the foster family?)
* Negative: verb "to be" + not going to (e.g. I'm not going to sign any paperwork if I don't get promotion).
6/ *
Future Tense (will):*
Action in the future that cannot be influenced (e.g. He will die no matter what).
*
Spontaneous decision (e.g. Any dog will logically counterattack roguishly if attacked).
*
Assumption with regard to the future (e.g. The military will get prepared if ever threatened by WW III).
--> Conjugation:
* Affirmative: will + verb (-to).
* Negative: will not (won't) + verb (-to).
* Interrogative: will + subject + verb (-to).
7/ *
Conditional Simple:*
An action that might take place (e.g. Under LSD's influence, the narrator would kill anyone in front of him).
--> Conjugation:
* Affirmative: would + verb (-to).
* Negative: would not (wouldn't) + verb (-to).
* Interrogative: would + subject + verb (-to).
* Well, I tried to explain the most commonly used tenses and provide two attached files herewith for your benefit. Talking with depth about these tenses would take ages, hence, I wanted to simplify things. I hope you get to benefit.

Post_3.png
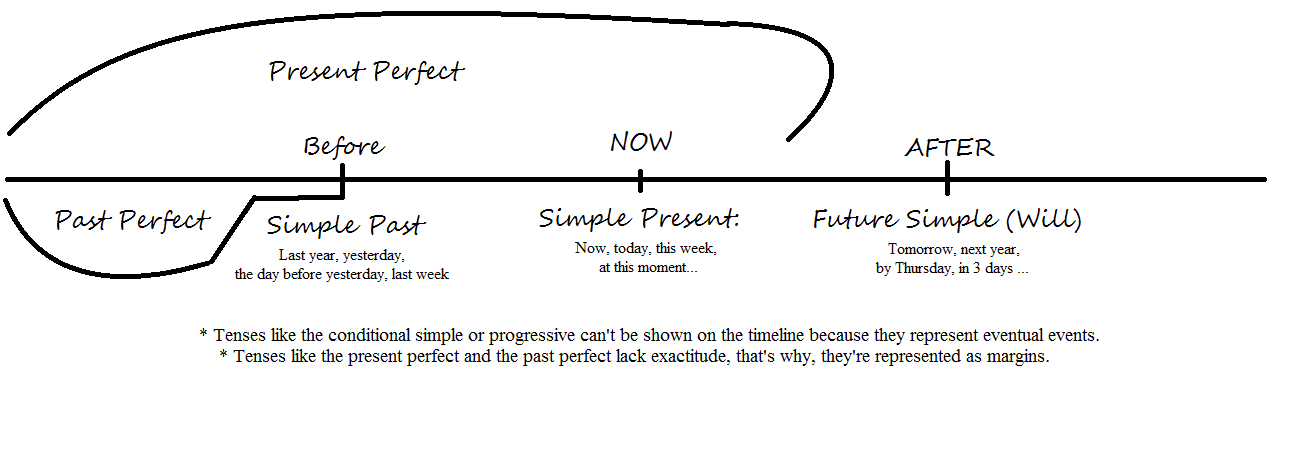
The tenses' time line and their positions herein


