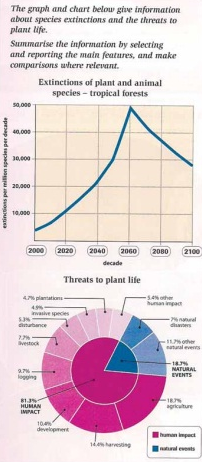
A comparison of the extinction's number of plant and animal species per million in a century and the percentage of threats to plant life between 2000 and 2100, a 100-year decade is illustrated in the line graph and the pie chart. Overall, the level of extinction is relied on enormous factors. In any case, while the graph experiences in-depth information about endangered plant and animal species in tropical forests, the chart shows some factors which threaten the plant's existence.
An observation reveals a significant change in the level of plant and animal extinction. In 2000, about 4,000 million species died -the lowest figure for the extinction. What is more, this worrying condition will increase dramatically twenty years later at 10,000 million species. The following 40 decades, this figure is predicted to peak at fifty thousand million species, which is the highest proportion for such extinction. Fortunately, in the last year of question period, the extinction's level is forecast to be a downward trend.
However, some factors threaten plant survival. Obviously, human impacts are higher than natural events. Over three quarter of extinction is caused by human activity, whilst only a fifth threatens come from natural incidents. Agriculture (18.7%) and harvesting (14.4%) are huge impacts which damage plant life. Meanwhile, only 7 percent and 11.7 percent of natural disasters and other events can threaten plant existence. Had the threats of both categories had been decreased, the existence of plant would not been a crucial issue.
An observation reveals a significant change in the level of plant and animal extinction. In 2000, about 4,000 million species died -the lowest figure for the extinction. What is more, this worrying condition will increase dramatically twenty years later at 10,000 million species. The following 40 decades, this figure is predicted to peak at fifty thousand million species, which is the highest proportion for such extinction. Fortunately, in the last year of question period, the extinction's level is forecast to be a downward trend.
However, some factors threaten plant survival. Obviously, human impacts are higher than natural events. Over three quarter of extinction is caused by human activity, whilst only a fifth threatens come from natural incidents. Agriculture (18.7%) and harvesting (14.4%) are huge impacts which damage plant life. Meanwhile, only 7 percent and 11.7 percent of natural disasters and other events can threaten plant existence. Had the threats of both categories had been decreased, the existence of plant would not been a crucial issue.
extinction_of_plant_.png
