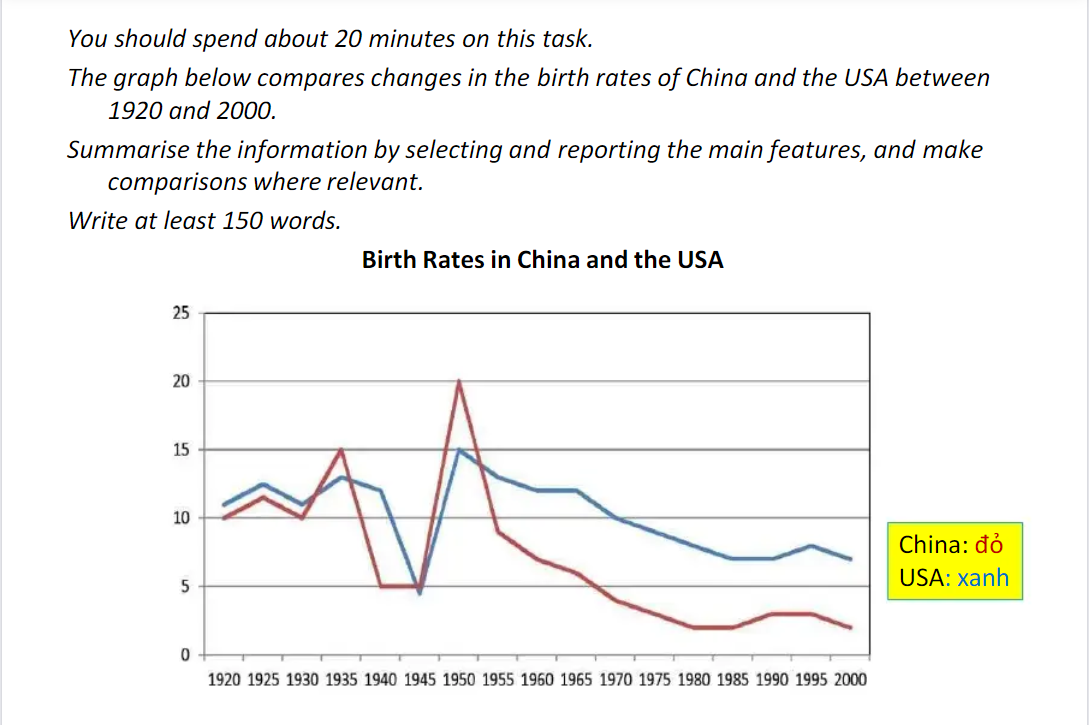
The line graph shows the proportion of birth in China and The USA from 1920 to 2000.
As can be seen from the graph, China and the US experienced a global downward trend by varying degrees.
Despite of a slight increase of 5 percent between 1920 and 1935, the percentage of baby boom in the US recorded a sharp decrease by 10 percent in the next 5 years, before reaching a peak of 20 percent at 1950. The figure indicated that a rapid fall in rate of birth in The US from 20 to nearly 2 percent was observed from 1950 on-ward.
At the 5 year start, the ratio of giving birth in China stabilized around 13 percent, however, in the period 1935 to 1945 saw a plummet of babies to 5 percent. US and China had a similar pattern in the 5 years after which has characterized by rocket of 10 percent in the rate of birth, before a sharp drop to 6 percent was undergone after that.
A further point of interest that in 1950 both of US and China came top of the list, they as well as had downward trend in the final time.
As can be seen from the graph, China and the US experienced a global downward trend by varying degrees.
Despite of a slight increase of 5 percent between 1920 and 1935, the percentage of baby boom in the US recorded a sharp decrease by 10 percent in the next 5 years, before reaching a peak of 20 percent at 1950. The figure indicated that a rapid fall in rate of birth in The US from 20 to nearly 2 percent was observed from 1950 on-ward.
At the 5 year start, the ratio of giving birth in China stabilized around 13 percent, however, in the period 1935 to 1945 saw a plummet of babies to 5 percent. US and China had a similar pattern in the 5 years after which has characterized by rocket of 10 percent in the rate of birth, before a sharp drop to 6 percent was undergone after that.
A further point of interest that in 1950 both of US and China came top of the list, they as well as had downward trend in the final time.
task1trend..png
