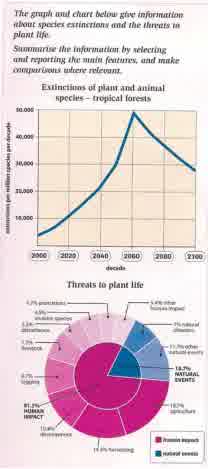
A comparison of the endangered plant and animal species in tropical forests over following a century between 2000 and 2100, is measured by per million species per decade and this is illustrated by the graph while, the chart describes regarding the factors which threaten plant life and is gauged by the percentages. Overall, a decrease number is predicted in the last four-decade period since the behaviour of human plays the vital impact based on the data.
First in all, a significant increase of the number species occurs for a half decade later. This is proved that in 2000, the rate of extinction flora and fauna stood at 5,000 in millions. Then, the trend always rise significantly until reach a peak by tenfold in 2,060. Suddenly, this decrease extremely approximately under 30,000 in the last year.
Moving to a more detailed analysis, although the natural events influence to the threating creatures, the immense aspect which affect is human being factors. The natural incidents like disasters solely causes around a quarter in extinction. Furthermore, the agriculture, harvesting and development have the high proportion in people activities with each 18.7%, 14.4%, and 10.4% respectively.
First in all, a significant increase of the number species occurs for a half decade later. This is proved that in 2000, the rate of extinction flora and fauna stood at 5,000 in millions. Then, the trend always rise significantly until reach a peak by tenfold in 2,060. Suddenly, this decrease extremely approximately under 30,000 in the last year.
Moving to a more detailed analysis, although the natural events influence to the threating creatures, the immense aspect which affect is human being factors. The natural incidents like disasters solely causes around a quarter in extinction. Furthermore, the agriculture, harvesting and development have the high proportion in people activities with each 18.7%, 14.4%, and 10.4% respectively.
tropical_forest.jpg
