The reading and the lecture are attached with the essay
Both the passage and the lecture relate to the migration hypothesis, which says that the elephant-sized edmontosaurs survived the winter by migrating south. On the one hand, the passage mentions three reasons supporting this hypothesis, while the lecture refutes all these reasons by saying that they are not convincing.
First of all, the passage states that the edmontosaur's food supports the migration hypothesis. Edmontosuars only eat plants and because there would have been no plants in the North Slope winter, it proves that the edmontosaurs must have migrated to warmer area to find food. In contrast, the lecture disagrees by saying that the edmontosaurs did not migrate for food. North Slope's temperature during the winter was even higher than today. There was twenty four hour sun shining in the peak of summer, as the result, the plants would grow in good condition. Moreover, in the winter, edmontosaurs would live on the nutrient of dead plants.
In addition, the passage goes on to say that the edmontosaurs lived in herd. Many migratory animals such as buffalo, caribou also live in herd in order to coordinate their migration. On the other hand, the lecture emphasizes that the edmontosaurs lived in herd not because of migration, but in order to have the protection against the predators. The lecture also mentions the elks in America, which live in herb but they do not migrate.
Last but not least, the passage asserts that edmontosaurs were capable of migrating long distances. They could use their locomotive power to increase their speeds to move to warmer region. Nevertheless, the lecture disputes this point by claiming that the young edmontosaurs could not run at speeds up to forty-five kilometers per hour. These young edmontosaurs would slow the migrating process of the herd. As the result, the older ones did not leave the younger, so they would stay and survive during the winter in North Slope despite cold weather.
Both the passage and the lecture relate to the migration hypothesis, which says that the elephant-sized edmontosaurs survived the winter by migrating south. On the one hand, the passage mentions three reasons supporting this hypothesis, while the lecture refutes all these reasons by saying that they are not convincing.
First of all, the passage states that the edmontosaur's food supports the migration hypothesis. Edmontosuars only eat plants and because there would have been no plants in the North Slope winter, it proves that the edmontosaurs must have migrated to warmer area to find food. In contrast, the lecture disagrees by saying that the edmontosaurs did not migrate for food. North Slope's temperature during the winter was even higher than today. There was twenty four hour sun shining in the peak of summer, as the result, the plants would grow in good condition. Moreover, in the winter, edmontosaurs would live on the nutrient of dead plants.
In addition, the passage goes on to say that the edmontosaurs lived in herd. Many migratory animals such as buffalo, caribou also live in herd in order to coordinate their migration. On the other hand, the lecture emphasizes that the edmontosaurs lived in herd not because of migration, but in order to have the protection against the predators. The lecture also mentions the elks in America, which live in herb but they do not migrate.
Last but not least, the passage asserts that edmontosaurs were capable of migrating long distances. They could use their locomotive power to increase their speeds to move to warmer region. Nevertheless, the lecture disputes this point by claiming that the young edmontosaurs could not run at speeds up to forty-five kilometers per hour. These young edmontosaurs would slow the migrating process of the herd. As the result, the older ones did not leave the younger, so they would stay and survive during the winter in North Slope despite cold weather.
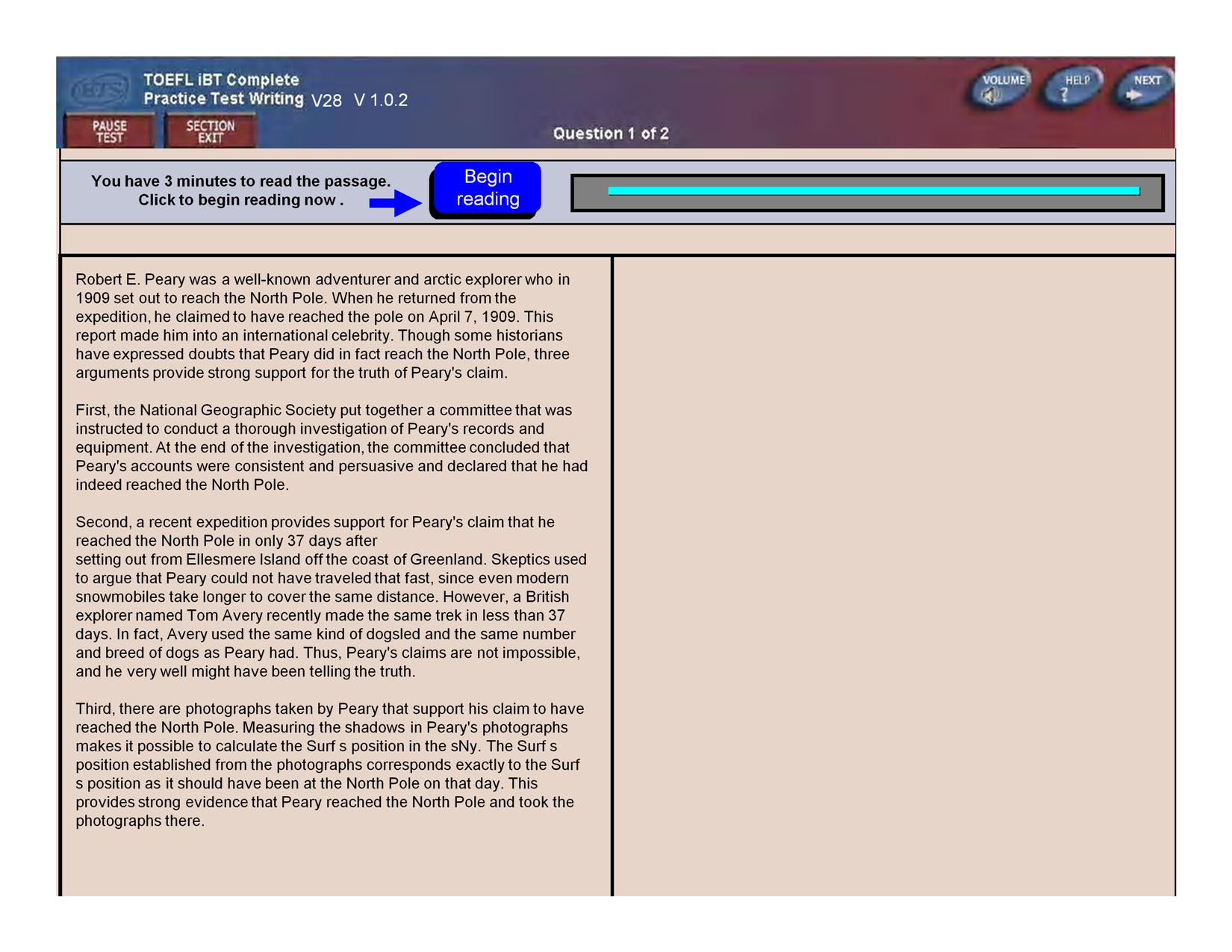
This is the reading
