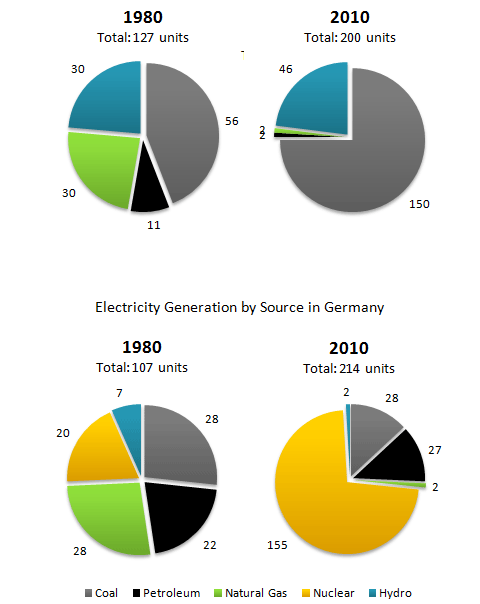
The pie charts below show electricity generation by source in New Zealand and Germany in 1980 and 2010.
The pie charts present about the proportion of 5 sources to electricity generation, namely coal, petroleum, Natural gas, nuclear, and hydro in 1980 and 2010. Overall, it can be seen that over the period coal was the biggest source was used in New Zealand. In contrast, the smallest source was petroleum and hydro in German.
In 1980, the most popular electricity generation in New Zealand was Coal at 56 units, and it saw an extremely increase to 150 units in 2010. It was also the main choice in by New Zealand citizens. However, just 28 units, it was no change in total units. Furthermore, Hydro was the second popular fuel was used in New Zealand from 1980 to 2010. It rose gradually from 30 to 40 units. In contrary, it became less popular in German.
In 2010, there was extremely downward trend of natural source in both of countries. They declined approximately 26 units, and then plummeted to 2 units in the latter period. On the other hand, the figure for petroleum in New Zealand decreased sharply from 11 to 2 during the period. Meanwhile, in German it inclined by 5 units, which reached at 25 units. (197w).
The pie charts present about the proportion of 5 sources to electricity generation, namely coal, petroleum, Natural gas, nuclear, and hydro in 1980 and 2010. Overall, it can be seen that over the period coal was the biggest source was used in New Zealand. In contrast, the smallest source was petroleum and hydro in German.
In 1980, the most popular electricity generation in New Zealand was Coal at 56 units, and it saw an extremely increase to 150 units in 2010. It was also the main choice in by New Zealand citizens. However, just 28 units, it was no change in total units. Furthermore, Hydro was the second popular fuel was used in New Zealand from 1980 to 2010. It rose gradually from 30 to 40 units. In contrary, it became less popular in German.
In 2010, there was extremely downward trend of natural source in both of countries. They declined approximately 26 units, and then plummeted to 2 units in the latter period. On the other hand, the figure for petroleum in New Zealand decreased sharply from 11 to 2 during the period. Meanwhile, in German it inclined by 5 units, which reached at 25 units. (197w).
291815_1_o.png
