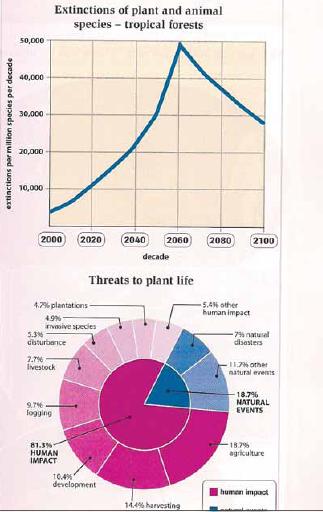
The line graph provides information on the proportion of plant and animal species will extinct between 2000 and 2100 projected year, a hundred-year period and the pie chart illustrates details about threats to plant life in tropical forest. The number of extinction species is forecast to increase steadily by decade. In any case, the majority of threats for plant life are caused by human impact.
The trend shows the change every 20 years from 2000 to 2100. The number of extinction species stood at 5000 in 2000. However, over the following six projected decades, this figure rise dramatically and reach a peak of 50.000. However, the graph predicts after this period the projected trend will be consistently plummeting, and finish with less than 30000 million over the remainder of the period.
On the other hand, plant has its threat from two main resources, human impact and natural events. It is obviously that more than 80 per cent damages are caused by human and 18.7% by natural events like disaster. Specifically, in agriculture sector and its activities (plantation and harvesting) have made 37.8% threats. Logging and other forms of humans' error are believed as hazardous activities for plant life
The trend shows the change every 20 years from 2000 to 2100. The number of extinction species stood at 5000 in 2000. However, over the following six projected decades, this figure rise dramatically and reach a peak of 50.000. However, the graph predicts after this period the projected trend will be consistently plummeting, and finish with less than 30000 million over the remainder of the period.
On the other hand, plant has its threat from two main resources, human impact and natural events. It is obviously that more than 80 per cent damages are caused by human and 18.7% by natural events like disaster. Specifically, in agriculture sector and its activities (plantation and harvesting) have made 37.8% threats. Logging and other forms of humans' error are believed as hazardous activities for plant life
k_3.jpg
