Question: The chart shows the percentage of male and female teachers in six different types of educational setting in the UK in 2019. Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant.
Write at least 150 words.
Anwers
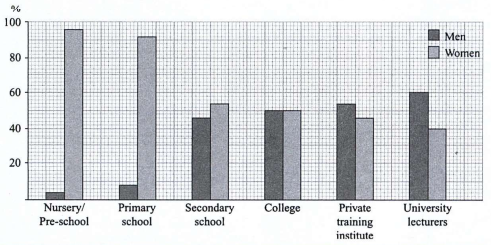
The given bar chart illustrates the gender distribution of educators among six distinctive types of UK educational institutions in 2019.
Overall, the proportion of female staffs surpassed that of male counterparts in lower educational levels, while men were more represented in higher education. In particular, a perfect gender balance was seen in college, highlighting the shift from female-preferred to male-preferred settings.
Regarding general education, women accounted for the vast majority of teachers in Nursery/Pre-school with roughly 95%, followed by Primary school educators at 90%, whereas the figures for male teachers were negligible with correspondingly 5% and 10%. In contrast, the gap between Secondary school women and men teaching staff narrowed significantly with the figures standing at 55% and 45%, respectively.
Turning to the higher stages of education, College teaching staff were equally at 50% for both genders. Beyond this educational level, the proportion of male instructors in private training institute held a slight lead at around 55%, closely followed by that of male University lecturers. On the contrary, female lecturers at University made up the smallest proportion of the figures at 40%, which was two-thirds that of their male counterparts.
Write at least 150 words.
Anwers
The given bar chart illustrates the gender distribution of educators among six distinctive types of UK educational institutions in 2019.
Overall, the proportion of female staffs surpassed that of male counterparts in lower educational levels, while men were more represented in higher education. In particular, a perfect gender balance was seen in college, highlighting the shift from female-preferred to male-preferred settings.
Regarding general education, women accounted for the vast majority of teachers in Nursery/Pre-school with roughly 95%, followed by Primary school educators at 90%, whereas the figures for male teachers were negligible with correspondingly 5% and 10%. In contrast, the gap between Secondary school women and men teaching staff narrowed significantly with the figures standing at 55% and 45%, respectively.
Turning to the higher stages of education, College teaching staff were equally at 50% for both genders. Beyond this educational level, the proportion of male instructors in private training institute held a slight lead at around 55%, closely followed by that of male University lecturers. On the contrary, female lecturers at University made up the smallest proportion of the figures at 40%, which was two-thirds that of their male counterparts.
b.png
