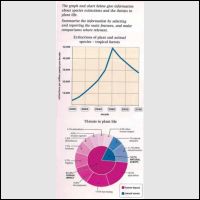
A breakdown which presents in the graph displays a prediction between 2000 and 2100 in the number of plants and animals species in the tropical forest which closed to extinction while the main causes of the extinction are displayed in the chart. The most noticeable fact is that the proportion of disappear species in the initial years is the lowest while in 2060 is forecast, It will reach a peak. Also, the main induces of the disappearance is caused by human impact.
A more detailed look at the graph reveals that in 2000, the quantity of extinction was in 5,000 species while from 2020 to 2040 onward, the proportion of disappearances are foreseen will growth significantly and will reach a boom by 45,000 figures. Meanwhile, in the 40 years future, the total number of figure will drop dramatically by 21,000 species.
When we look the main induces of the species extinctions, the human impact is the highest contribution to the disappearance at 81.3% while natural events donates at 18.7%. The proportion of treats which provide the highest donation to plant life is agriculture activities in 18.7% while the lowest contribution is plantations by 14%.
A more detailed look at the graph reveals that in 2000, the quantity of extinction was in 5,000 species while from 2020 to 2040 onward, the proportion of disappearances are foreseen will growth significantly and will reach a boom by 45,000 figures. Meanwhile, in the 40 years future, the total number of figure will drop dramatically by 21,000 species.
When we look the main induces of the species extinctions, the human impact is the highest contribution to the disappearance at 81.3% while natural events donates at 18.7%. The proportion of treats which provide the highest donation to plant life is agriculture activities in 18.7% while the lowest contribution is plantations by 14%.
baru.jpg
